UTIs are the second most common type of infection in the body.
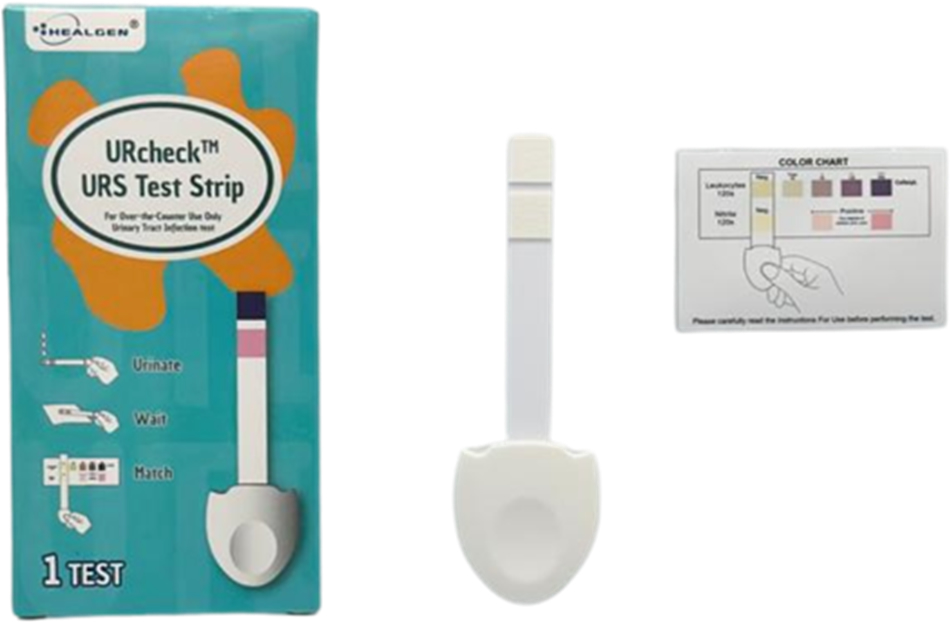

- A UTI is an infection within the urinary tract. This includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
- Bacteria, like E. coli, most commonly cause a UTI. The bacteria enter the urethra and spreads to the bladder. If not treated promptly, the infection can travel up to the kidneys and cause more serious problems.
- UTIs are very common, with estimates suggesting that over 50% of women will experience at least one UTI in their lifetime.
- Women are more likely to develop UTIs than men because women have a shorter urethra, that makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder.
- Common symptoms of UTIs include: an urgent need to urinate, a burning feeling when urinating, an aching feeling, pressure or pain in the lower abdomen or back, cloudy or blood-tinged urine and/or a strong odour to the urine.
- People most at risk for UTIs include: women (especially sexually active ones), older adults, individuals with diabetes, patients with catheters, people with urinary tract abnormalities like blockages or reflux, pregnant women and men with enlarged prostate glands.
- To help prevent UTIs: stay hydrated (drink plenty of fluids), empty the bladder promptly (avoid postponing going to the bathroom for extended amounts of time), empty the bladder completely before going to sleep and go to the toilet after sex (urinating soon after intercourse can help prevent bacteria from spreading).
- Women, specifically, should wipe from front to back after going to the bathroom to prevent bacteria from the bowels from getting into the urinary tract.
- To diagnose a UTI, the healthcare provider will do a urinalysis. Urinalysis test a sample of the urine for signs of infection, such as bacteria, white blood cells (leucocytes) and nitrites.
- Avoid feminine hygiene sprays, douches, and scented or coloured bath products.